What pipes to choose for a warm water floor
Repairing a pipeline laid under a screed or inside a frame structure is a complex procedure. Therefore, the question of which pipe to choose for a warm floor is always relevant. Given that the range of pipes for underfloor heating is wide enough, it is advisable to imagine the selection criteria.
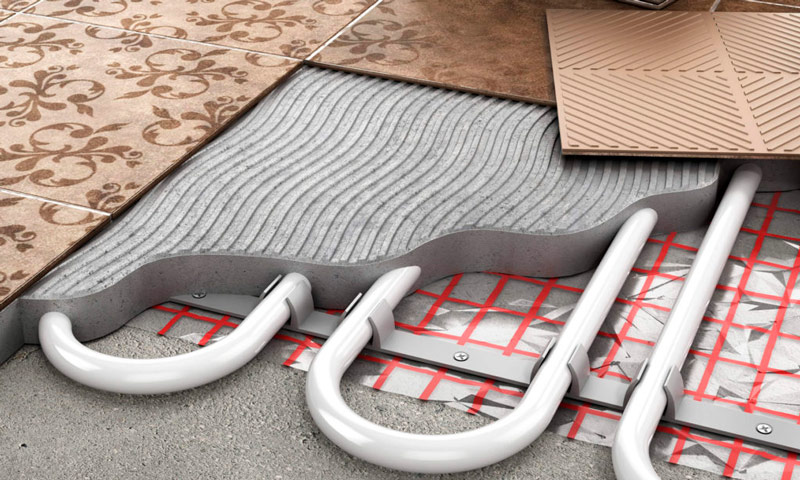

Requirements for underfloor heating pipes
Theoretically, any pipeline is suitable for transporting not too hot coolant. Even assembled from various scraps. But in cases where leaks are a serious waste of money, reliability becomes a determining requirement. This is an abstract, like longevity, concept, which includes a whole range of characteristics. Therefore, the simplest and most obvious recommendation is to use only specially designed pipes.
Temperature resistance
Resistance to temperatures, necessary even taking into account the fact that floor coverings do not heat up above 35 ° C. For heating, in any case, use materials that withstand heat up to 90 ° and above. This is due not only to peak values of temperature, but also to the continuity of exposure. The structure of materials not intended for this crystallizes if they are permanently heated to only 30-40 °, and collapses.
Mechanical strength
Pipes must have mechanical strength sufficient to contain internal pressure, the weight of the concrete screed, various deformations, and the erosive effects of water. As a rule, the pressure in the heating systems of private houses does not exceed 2 atm., But the pipe must withstand at least 6 atm. This indicator will include almost any load.
Chemical inertness
Chemical inertness, including resistance to oxygen, electrochemical corrosion, coolant components, as well as aggressively alkaline environment formed by cement.
Sufficient pipe length
The length of an individual pipe section should be sufficient to lay a separate circuit. This is perhaps the main reason why steel is almost never used here, even from stainless steel. Any joint is a “weak link” in terms of strength and chemical inertness. Moreover, it violates the smoothness of the inner surface of the pipeline, reducing its permeability, increasing hydraulic losses.
Therefore, a pipe designed for underfloor heating is most often sold in long sections rolled into coils.
Pipe contour laying options
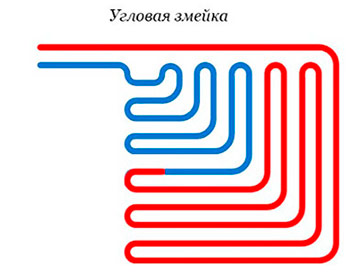
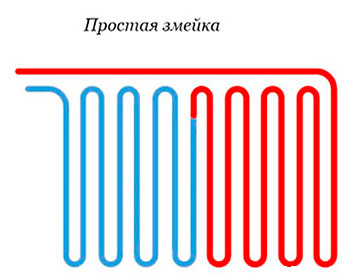
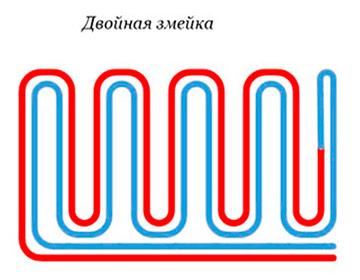
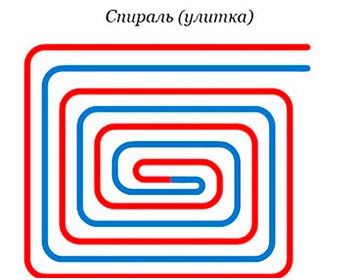
The quality of materials and components
The quality of materials and components, confirmed by certificates, the name of the manufacturer, customer reviews. Of course, no one is safe from fakes. But a well-known European brand will definitely be more reliable than the “left noname”. Although you can test the pipe yourself, subjecting it to any extreme loads.
Interchangeability, compliance of fittings to accepted standards
An unknown small producer will not be able to saturate the market with them. Buying a cheap pipe, albeit a good one, is only half the battle. Without high-quality fittings, which there is nothing to replace, it is completely useless.
Another significant nuance is oxygen diffusion.SNiP 2.04.05-91 explicitly says that the heating system pipeline must contain an anti-diffusion layer (oxygen barrier), which prevents air from entering the system. We are talking about polymer pipes - plastic (metal-plastic), polypropylene, polyethylene.
However, opponents of this assertion make their case. For example, that even in a closed system the appearance of oxygen is inevitable. Therefore, a more important task is its effective elimination. A safe, reliable way is the installation of air vents and (or) deaerators. You can also add hygroscopic additives - toxic hydrazine or sodium sulfite, but their content must be controlled.
Important: thermal conductivity is also a controversial parameter. It becomes key only if rapid warming up is required, significant heat loss is present or the heat removal area is insufficient.
What type of pipe is better to use for a warm floor
Obviously, universal underfloor heating does not exist, and each type of pipe is distinguished by its own characteristics. A good way to save money without risking anything is to make informed, informed choices. In addition, there is practically no shortage now, and all information is in the public domain.
Copper pipes
Copper is a refractory non-ferrous metal that has been used for pipeline production for more than a thousand years. The durability of these products has long been confirmed and practically does not cause disputes. For the installation of modern heated floors, copper pipes are used in pure form or in a PVC shell.

Copper pipe.
PVC-coated copper pipes are specially designed for this purpose and, with some reservations, meet all the requirements. However, recently, due to the availability of polymeric materials, copper rolling is losing popularity. But this does not detract from its merits.
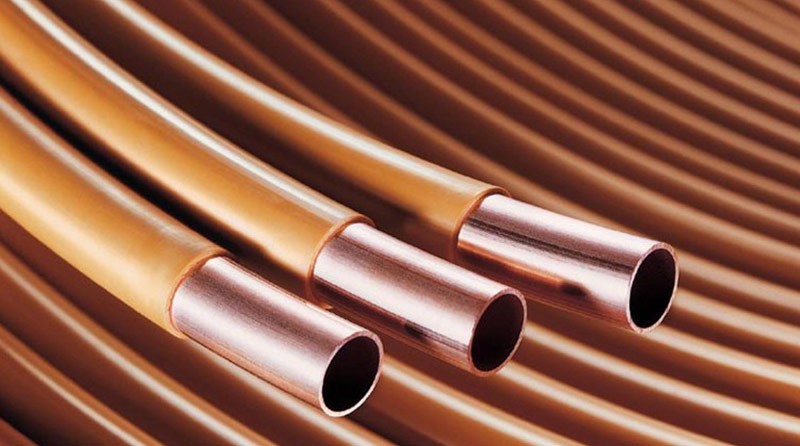

Copper pipe in PVC sheath.
Moreover, the total price of copper underfloor heating is twice or three times the cost of systems made of other materials. For example, from polypropylene or polyethylene. However, copper pipes have flaws that often confuse the consumer more than the price.

The advantages of a copper pipe
- resistance to continuous, discrete or sudden exposure to high temperatures and UV radiation;
- resistance to oxygen corrosion due to the formation of an oxide film (patina);
- strength to withstand pressure, depending on the diameter, up to 80 atm .;
- smoothness of the inner surface (subject to proper installation);
- ease of processing, styling;
- simplicity and reliability of connections - crimp or soldering (welding is possible, but not recommended in this case);
- the length of the pipe (annealed) in the bay, as a rule, is sufficient for seamless laying of hidden sections;
- resistance to the influence of the cement medium and mechanical stresses (limited, only in the presence of a protective sheath);
- high thermal conductivity, even in the shell;
- impermeability to oxygen diffusion;
- flexibility (for "annealing"), providing a minimum bend radius;
- prevalence, "standard" components;
- environmental safety, antiseptic properties.

Cons of copper pipe rolling
- high rate of destruction due to electrochemical corrosion;
- poor resistance to strong acid or alkaline environments, for example, ammonia additives in the coolant;
- low resistance to erosion and other mechanical stresses with improper installation.
Despite the seriousness, these factors are offset by compliance with the rules of installation and operation. For example, you can not use too hard or soft water, any chemistry, dock copper with steel or zinc. In addition, metal pipelines, including copper, must be grounded, and oxygen from them must be removed.
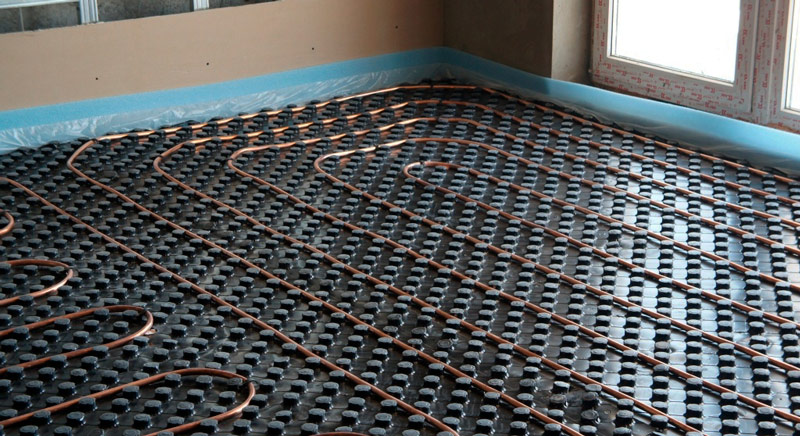

Warm floor made of copper pipe.
Please note: in Europe and North America, stainless steel and copper are the most popular materials for heating systems. Including water underfloor heating.
Plastic pipes
The sectional metal-plastic pipe is a “sandwich” of 3 layers. Its core is aluminum foil, 0.3-0.5 mm thick. It strengthens the structure, simplifies the formation of bends and prevents oxygen diffusion.
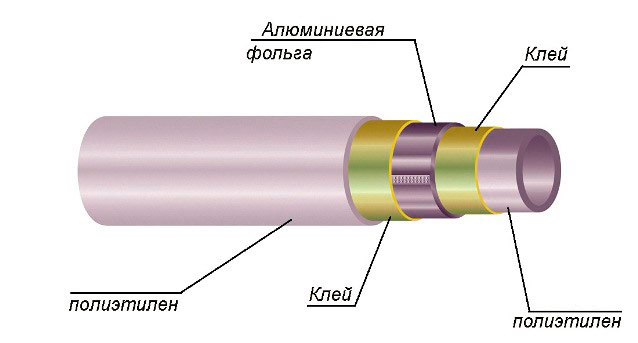
The device is a plastic pipe.
The inner and outer layers are the polymer responsible for the tightness and spatial stiffness of the pipe. It can be made of ordinary, cross-linked or heat-resistant polyethylene. Finding out which pipes are better for a warm floor, often mean the last two options.
Thanks to the good characteristics of the metal-plastic pipe, installation can be handled without even having special skills and equipment. You only need a general idea of the process, a hacksaw for metal and a pair of adjustable wrenches.

The advantages of the pipeline from metal
- low price;
- declared service life of up to 50 years (subject to the rules of installation and operation);
- resistance to heating up to 90 ° C (short-term) at water pressure up to 6-8 atm .;
- resistance to all types of corrosion;
- hygiene, safety, aesthetics;
- strength combined with elasticity;
- simplicity of processing and installation;
- smoothness of the inner surface;
- lack of electrical conductivity;
- lack of oxygen diffusion;
- the length of the whole “whip”, in most cases sufficient for seamless laying of hidden areas;
- a small bend radius equal to 6-8 pipe diameters, and retention of the obtained shape.

Cons of a metal-plastic pipeline
- high coefficient of thermal expansion, which reduces the reliability of the collet connection and causes friction against solids (for example, screed);
- cost of fittings;
- the cost of the tool to make reliable press crimp connections;
- high dependence of service life on the combination of temperature, pressure and the frequency of their impact;
- lack of resistance to UV radiation, high temperatures (exceeding declared values);
- inadmissibility of excesses, fractures;
- low thermal conductivity.
The list of shortcomings, it would seem, casts doubt on the appropriateness of the use of metal plastic. However, compliance with the rules of installation and operation in most cases reduces their importance. In addition, some negative factors can become neutral.
For example - low thermal conductivity, due to which it is necessary to reduce the flow rate, increase the diameter of the pipe, increase the temperature of the water. Such a pipeline does not make noise, and even a not very powerful pump can handle circulation.
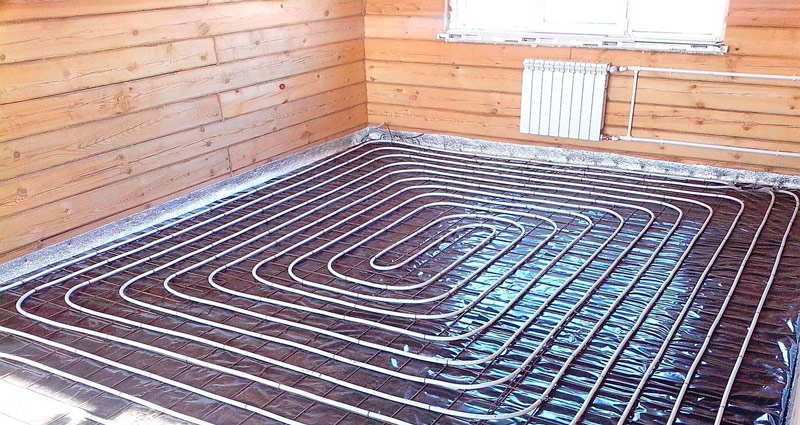

Warm floor made of plastic pipe.
Polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene is a less dense and elastic polymer than polyethylene, so the pipeline is made of it more thick-walled. This affects all the properties of polypropylene pipes, making them less suitable for underfloor heating. However, heat-resistant modifications (PPB, PPR, PPRC), reinforced with fiberglass or a continuous anti-oxygen layer, are successfully used for the assembly of heating systems. One way or another, these products are popular in Russia.
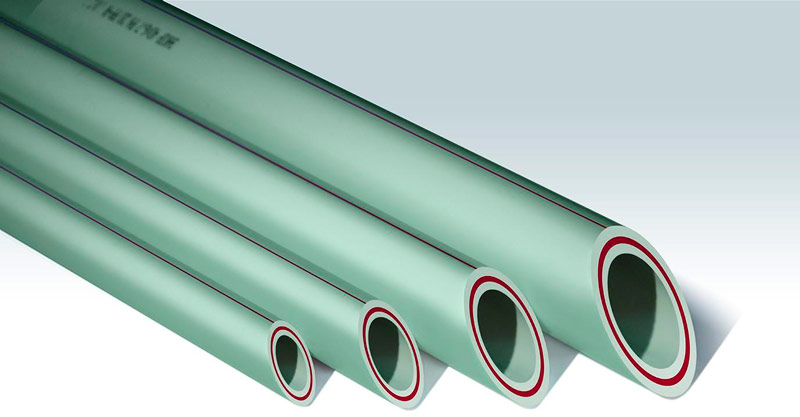

Polypropylene pipes.

The advantages of a polypropylene pipeline
- price, availability;
- simplicity, reliability of installation, docking (soldering or gluing);
- resistance to temperature influence up to 90 ° (short-term, only for types PPB, PPR, PPRC, not lower than the second class);
- resistance to all types of corrosion;
- chemical inertness (conditional, excluding, for example, strong oxidizing agents);
- service life up to 50 years (if used correctly);
- strength (limited);
- safety, aesthetics, dielectric;
- lack of oxygen diffusion (for models whose design includes an oxygen barrier);
- small roughness of the inner surface (with the correct connection).

Cons of polypropylene
- pronounced dependence of durability on the duration of exposure to peak temperatures and high pressure;
- limited length of seamless sections due to the size of the pipe (it is usually no longer than 4 m), as well as the undesirability of bending
- reduction in the passage of the pipeline at the joints;
- significant thermal expansion, increasing loads in places of contact with solid objects;
- the lowest thermal conductivity of all types of pipes used for heating systems;
- intensive penetration (diffusion) of oxygen through the walls in most PP-pipe models;
- rapid aging with abundant saturation of the coolant with oxygen and high temperature;
- lack of resistance to UV radiation, frost, mechanical damage, as well as temperatures exceeding permissible values.
It is worth adding that polypropylene pipes, at least unreinforced, bend quite easily (when heated to 100-140 °). But manufacturers, as a rule, do not talk about this, because such a bend worsens the characteristics of the product. In this case, for example, the pipe wall becomes thinner, the cross section decreases, the roughness increases, and the destruction of the material is likely.
Despite the advantages of polypropylene, its disadvantages are so serious that the material is practically not used for underfloor heating. Although in small rooms - bathrooms, kitchens, hallways - there are no obvious prerequisites for refusal. But there are no advantages over other types of pipeline either.
Stainless steel corrugated pipe
Stainless steel corrugated pipes are ribbed products made of a thin (0.3-0.5 mm) stainless steel sheet. They can be annealed or unannealed, which affects elasticity and cost (the former are better and more expensive). They are used for hot, cold water supply, as well as in the assembly of heating systems. In particular, they are suitable for underfloor heating.
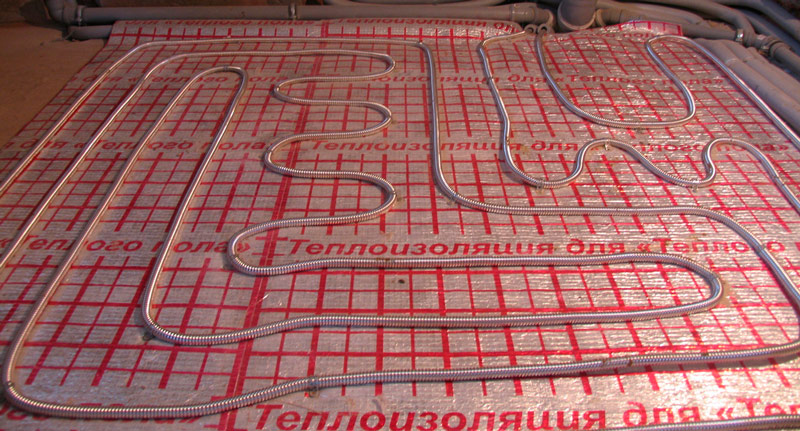
Warm floor made of corrugated pipes.
Corrugated pipes in a polyethylene sheath are additionally protected from external aggressive influences.

Stainless steel corrugated pipe in a polyethylene shell.
Corrugated stainless steel pipes allow quick and reliable connections thanks to special fittings.
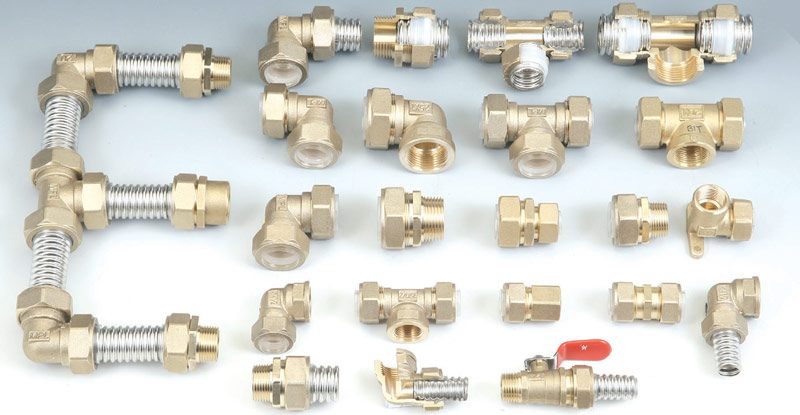
Stainless Steel Corrugated Pipe Fittings.

Advantages of Corrugated Stainless Steel Pipe
- unlimited service life and resistance to all types of corrosion;
- chemical inertness (in the absence of oxygen, other strong oxidizing agents and alkalis);
- resistance to high temperatures (up to 100 ° C) at a pressure of up to 15-17 atm. for a long time (service life);
- short-term resistance to peak loads - up to 50 atm. or 200 ° C;
- impermeability to oxygen diffusion;
- resistance to UV radiation and external contacts (in the shell);
- resistance to defrosting;
- high thermal conductivity;
- minimal thermal expansion;
- ease of installation, reliable connections;
- small bend radius (3-4 pipe diameters);
- uselessness of special equipment;
- long pipe length in the bay;
- low surface roughness;
- the price, on average, is half that of copper.

Cons corrugated stainless steel pipes
- low resistance to electrochemical corrosion;
- inadmissibility of creases, excesses.
Corrosion resistance for this type of pipe is maintained provided that the coolant does not contain oxygen, dirt, sludge and active additives, other metals are not part of the system, and the system itself is qualitatively grounded or completely insulated.
The listed factors, in general, are obvious and arise from the properties of stainless steel as an alloy. However, the material has not yet gained wide popularity, apparently due to great competition. There have been few reviews of this type of pipeline since the beginning of distribution in Russia (the nineties of the twentieth century). Most of them are positive, but there are also negative ones.
PEX cross-linked polyethylene pipes
This is a large class of products, which includes, for example, the well-known three-layer metal plastic. But a pipe made of cross-linked polyethylene can consist of only two or even one layer. Indeed, it is polyethylene that bears the main load, and the interlayer performs an important, but, nevertheless, auxiliary function. It prevents the diffusion of oxygen and may not be metallic, but polymeric. Only the polymer here is special - EVOH.
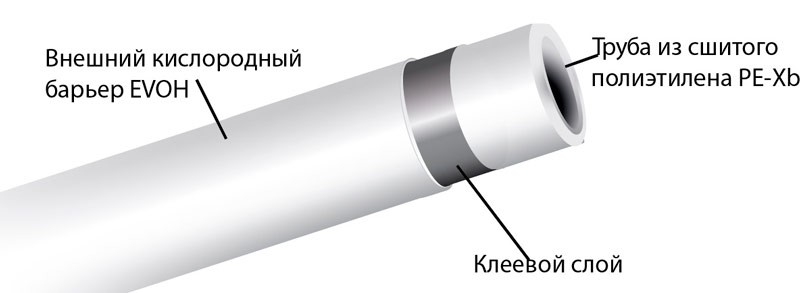
The device is a pipe made of cross-linked polyethylene.
Cross-linked polyethylene differs from ordinary polyethylene (PE) in a more durable, heat-resistant structure, reinforced by transverse intermolecular bonds. Staple it in four ways, so the marking of the pipe may look like “PEX-a”, “-b”, “-c” or “-d”. At the beginning of the century they simply indicated “PEX”. The most expensive and conditionally high-quality modification is PEX-a, the most popular is b, and the cheapest and probably hazardous to health are c, d. In the European Union, for example, the use of a PEX-c pipeline is prohibited.
| Type of pipe | stitching process | Minimum crosslink density |
|---|---|---|
| Pex-a | Peroxide | 75% |
| Pex-b | Silane | 65% |
| Pex-c | Radiation | 60% |
| Pex-d | Nitric | 60% |
However, in closed heating systems, the toxicity of polyethylene does not play a role, because the coolant is sometimes toxic. A more significant point is the fact of crosslinking, which is not always reliable. Although it is not difficult to check, you need to hold the product in the oven with a temperature of 120-150 ° C for 10-20 minutes. Qualitative material will not change at all, and ordinary polyethylene will melt.
Considering the ratio of price and quality, PEX are the best pipes for a warm water floor. Moreover, in such systems, the pipeline is operated, as a rule, in a sparing mode. That is, with a water temperature of not more than 45-50 ° C and a pressure not exceeding 2-2.5 atm. All the advantages of cross-linked polyethylene, especially two- or three-layer ones, are revealed here.

PEX Piping Advantages
- declared service life - up to 50 years (subject to installation and operation requirements);
- long (during the service life) resistance to moderately high temperature at a pressure of up to 5-6 atm .;
- short-term resistance to peak values - up to 95 ° C and 15 atm .;
- resistance to almost all types of corrosion (except for the effects of strong oxidizing agents, alkalis, concentrated hydrocarbons);
- resistance to UV radiation;
- thermal conductivity sufficient for a heat-insulated floor;
- lack of electrical conductivity;
- strength combined with flexibility and maintaining a given shape;
- quick, simple, reliable assembly by means of compression or press crimp connections;
- the length of a single piece in the bay, sufficient for seamless laying in large areas;
- low surface roughness, high water permeability;
- the price of some subspecies of the pipe is 10 times lower than that of copper.

Cons of cross-linked polyethylene pipe
- quick failure in case of violation of the operating rules (use of unsuitable coolant, too high temperature and pressure);
- significant thermal elongation, increasing the load in the places of friction;
- inadmissibility of "monopolizing" compounds;
- tool cost for crimp connections;
- a relatively large bend radius equal to 8-10 pipe diameters;
- the intensity of oxygen diffusion through the walls (for single-layer modifications).
It is worth noting that, as a rule, only the products of well-known large manufacturers exhibit the declared properties. On their own experience, by trial and error, they set all the necessary parameters for automated production. For example, the ratio of components, time intervals, temperature and pressure modes. Small companies ("noname"), as a rule, do not stand up to competition, worrying about quality. Still, such a production is not the easiest.
Despite the importance of the shortcomings, they are mainly conditional. For example, a two- or three-layer pipe, such as PEX-Al-PEX or PEX-EVOH, is not much more expensive than a single-layer PEX. However, the anti-oxygen layer gives a serious effect, protecting both the polyethylene itself and the metal components of the system. Other flaws in the technology can be circumvented by observing the rules and recommendations for installation and operation. For example, use only press crimp connections, protect the end parts of the pipeline (bend points) with soft gaskets, etc.
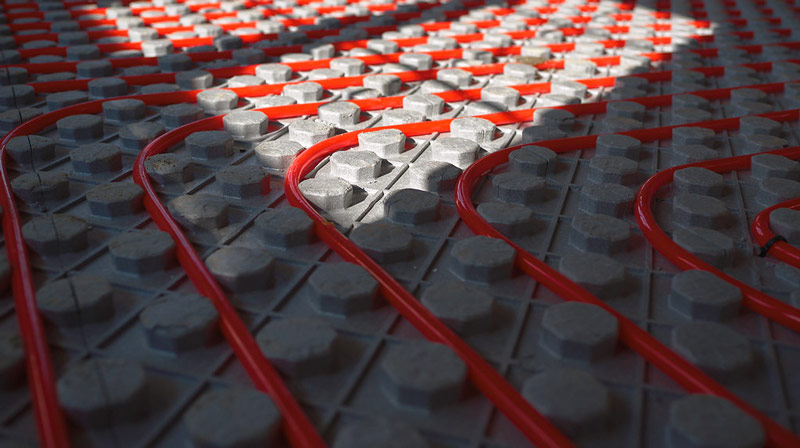
Warm floor made of PEX cross-linked polyethylene pipes.
Note: you can check the strength of the pipe by trying to break it or break it. A reliable sample, most likely, cannot be broken by hands.
High temperature resistant polyethylene pipes PE-RT
Heat-resistant polyethylene (PE-RT) is a polymer that differs from ordinary polyethylene in more branched bonds between the molecules. It is not crosslinked, since here these bonds are established during synthesis. Therefore, they are more uniform than, for example, in PEX-c material, but less stable than in PEX-a (or “b”).
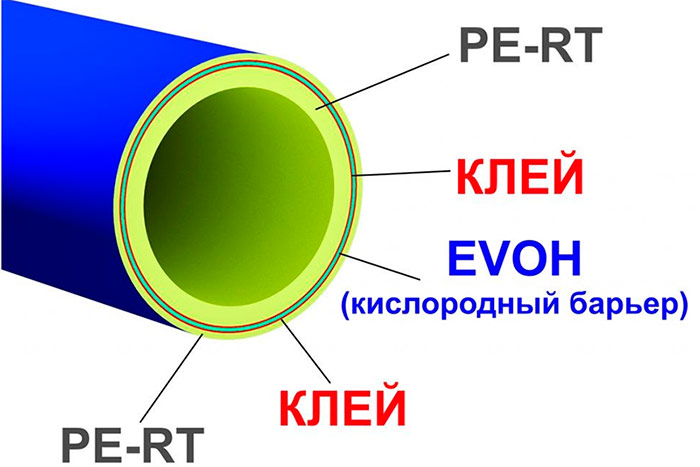
The device of a pipe from PE-RT polyethylene.

Advantages of the PE-RT pipeline
- availability (1.5-2 times cheaper than high-quality PEX);
- heat resistance limited by a set of operating conditions - up to 90 ° at 4-5 atm., up to 60 ° at 7-8 atm .;
- durability during the work in the sparing mode;
- UV resistance
- ease of installation, processing;
- sufficient pipe length in the bay;
resistance to almost everyone - types of corrosion (worse than PEX);
- strength (worse than PEX);
- surface smoothness.

Cons PE-RT
- unpredictable failure in case of non-compliance with the recommended modes
- temperature and pressure;
- intense oxygen diffusion;
bending radius equal to 10-12 pipe diameters; - significant expansion (elongation) when heated;
Of course, when it comes to the fact that PE-RT is somewhat worse than PEX, the products of the same manufacturer are roughly equal in class. Here you can highlight the indicator, which sometimes becomes decisive - the price. Given that the fittings are the same (at least “slide sleeves”), the savings will be substantial. Although this fact depends, first of all, on the volume of work.

Warm floor made of PE-RT pipe.
What to look for when choosing a pipe for a warm floor
First of all, it is necessary to imagine the conditions for laying and operating the future warm floor in a broad sense. For example, the severity of winter, heat loss at home, the area of the premises, the installation of the heating system, the type of flooring. Narrower and more specific points depend on these parameters. Including - temperature, pressure, circuit length, etc. And the characteristics of the elements of the heating system depend on these values.
For example, if a frame structure is planned instead of a screed, the effects on the pipeline will be softer. Hence, a protective sheath for the pipe is optional. But then thermal conductivity becomes a more significant factor, because heat transfer by air is less effective than the body of concrete. In this case, it is worth considering copper or stainless steel corrugated pipe.
If screed construction is planned on top of the warm floor, in this case metal-plastic pipes are most often used.
When choosing a pipe for a warm floor, it is advisable to pay attention to the following main parameters:
- strength, expressed in the recommended and maximum allowable pressure in the system;
- resistance to heat, also indicated in the recommended and maximum values;
- the service life declared by the manufacturer, as well as its relationship with the operating mode;
- thermal conductivity;
- electrical conductivity;
- resistance to oxygen diffusion, expressed in the presence of an anti-oxygen layer (only for polymers);
- chemical and corrosive activity, expressed in the list of substances, contact with which should be excluded;
- installation specifics;
- manufacturer reputation.
The last point often becomes a key one, because even the most accurate calculation will break into low-quality materials. And sometimes it is not possible to determine the quality. Then the name of the manufacturer is the only indicator confirming the reliability of information on the characteristics of products and justifying the ratio of price and quality.
Large companies that have long been on the market take care of their reputation, provide a guarantee, take care of the availability of certificates of quality and product safety. For example, brands such as Rehau, Valtec, Fado, Icma, Uponor, Tece, Ekoplastik, Kan and Aquapex are certified in Europe and, most importantly, have long established themselves only on the positive side.




